Deep TMS vs TMS
As mental health treatments continue to evolve, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a promising non-invasive therapy for conditions like major depressive disorder (MDD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). There have been many innovations in this field over the last decades, with new techniques offering better results, shorter procedure time, and higher safety. Traditional TMS and Deep TMS represent two distinct approaches to brain stimulation therapy, each with unique characteristics and benefits. While both technologies use magnetic fields to stimulate neural activity, their mechanisms, effectiveness, and treatment protocols differ significantly and are worth exploring.
As mental health treatments continue to evolve, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a promising non-invasive therapy for conditions like major depressive disorder (MDD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). There have been many innovations in this field over the last decades, with new techniques offering better results, shorter procedure time, and higher safety. Traditional TMS and Deep TMS represent two distinct approaches to brain stimulation therapy, each with unique characteristics and benefits. While both technologies use magnetic fields to stimulate neural activity, their mechanisms, effectiveness, and treatment protocols differ significantly and are worth exploring.
What Is Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS)?
Procedure
What Is Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)??
Procedure
Differences Between Deep TMS and rTMS?
Treatment Depth
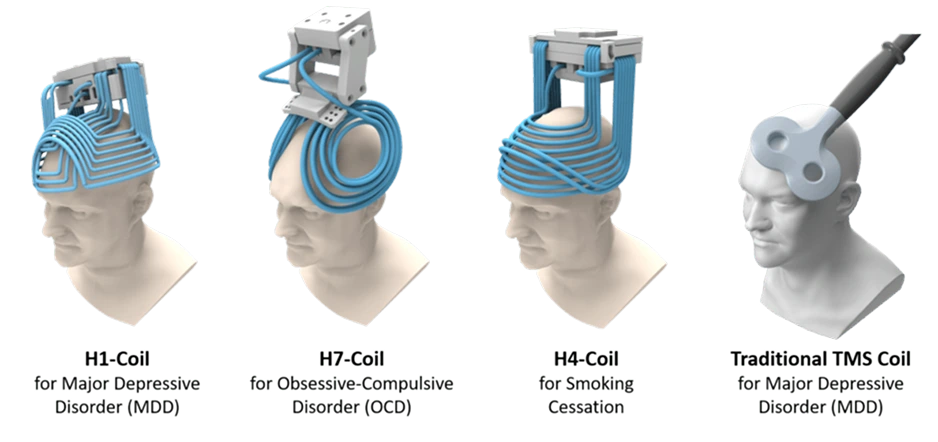
Coil Type
- The H1 coil is designed for treating MDD, anxious depression, and late-life depression.
- The H4 coil specifically targets neural pathways associated with smoking addiction.
- The H7 coil has demonstrated effectiveness in treating major depression, OCD, and anxious depression.
FDA Approvals
Session Duration
Targeted Brain Regions
Side Effects
Both Deep TMS and rTMS are considered significantly safer alternatives to more invasive treatments like vagus nerve stimulation, electroconvulsive therapy, or deep brain stimulation. TMS side effects are generally mild and transient, including scalp discomfort and occasional headaches that typically diminish after the first few sessions. While both treatments share similar safety profiles, Deep TMS patients might experience slightly more adverse reactions due to the broader stimulation zone. However, this difference is minimal and usually well-tolerated. Importantly, neither treatment carries the cognitive side effects often associated with medications or more invasive procedures. Patients can resume normal activities immediately after each session.
Efficacy for Specific Conditions
Clinical studies have demonstrated varying response rates between Deep TMS and rTMS across different conditions. Both technologies show significant therapeutic benefits. Understanding these distinctions in treatment outcomes can help you make informed decisions about your journey toward mental wellness:
- Deep TMS: 80% response rate
- rTMS: 40-60% response rate
- Deep TMS: 38-73% response rate
- rTMS: 58% response rate
- Deep TMS: 28% quit rate at 1 month
- rTMS: 23.8% quit rate at the target date
Equipment Design
The physical configuration of the two technologies reflects their distinct approaches to brain stimulation. Deep TMS utilizes a helmet-like device containing the H-coil, which encompasses a more significant portion of the patient’s head and provides more comprehensive coverage. This design allows for a more comfortable and stable treatment experience, as the helmet maintains consistent positioning throughout the session. In contrast, rTMS employs a more compact figure-8 coil mounted on an articulating arm, requiring precise positioning and maintenance of the location during sessions. While both systems include sophisticated cooling mechanisms and computerized control interfaces, the Deep TMS helmet design offers more stability and potentially reduces the need for continuous adjustments during procedures.
Deep TMS vs. rTMS: A Summary
Feature
Deep TMS
rTMS
Penetration Depth
Up to 4 cm beneath the skull
Nearly 0.7 cm beneath the skull
Coil Type
H-coil with a broader magnetic field
Figure-8 coil with focused magnetic field
FDA Approvals
MDD, OCD, anxious depression, smoking addiction, late-life depression
MDD, OCD, anxious depression, adolescent depression
Session Duration
20-40 minutes, depending on the protocol
18-40 minutes with accelerated options
Targeted Brain Regions
Broader coverage of multiple neural networks
Focused targeting, primarily DLPFC
Side Effects
Mild discomfort, headaches, muscle twitches, lightheadedness.
Mild discomfort, headaches, muscle twitches, lightheadedness
Efficacy (MDD)
80% response rate
40-60% response rate
Efficacy (OCD)
38-73% response rate
58% response rate
Efficacy (Smoking Cessation)
28% quit rate at 1 month
23.8% quit rate at target date
Equipment Design
Helmet-like device with stable positioning
Compact coil mounted on an articulating arm
Deep TMS
rTMS
Penetration Depth
Up to 4 cm beneath the skull
Penetration Depth
Nearly 0.7 cm beneath the skull
Coil Type
H-coil with a broader magnetic field
Coil Type
Figure-8 coil with focused magnetic field
FDA Approvals
MDD, OCD, anxious depression, smoking addiction, late-life depression
FDA Approvals
MDD, OCD, anxious depression, adolescent depression
Session Duration
20-40 minutes, depending on the protocol
Session Duration
18-40 minutes with accelerated options
Targeted Brain Regions
Broader coverage of multiple neural networks
Targeted Brain Regions
Focused targeting, primarily DLPFC
Side Effects
Mild discomfort, headaches, muscle twitches, lightheadedness.
Side Effects
Cognitive enhancement, motor learning, stroke rehab, chronic pain, and depression.
Efficacy (MDD)
80% response rate.
Efficacy (MDD)
40-60% response rate
Efficacy (OCD)
38-73% response rate
Efficacy (OCD)
58% response rate
Efficacy (Smoking Cessation)
28% quit rate at 1 month
Efficacy (Smoking Cessation)
23.8% quit rate at target date
Equipment Design
Helmet-like device with stable positioning
Equipment Design
Compact coil mounted on an articulating arm
Which One Is Better for Treating Major Depressive Disorder?
When evaluating the effectiveness of these technologies in treating depression, clinical evidence suggests that Deep TMS may hold a slight advantage. Its ability to stimulate broader and deeper brain regions has demonstrated higher efficacy in reducing depressive symptoms, with studies showing response rates of up to 80% compared to rTMS’s 40-60%. However, individual patient factors, such as the severity of the condition, previous treatment history, and specific symptom patterns, play crucial roles in determining the most appropriate therapy choice. Both technologies represent significant advances in non-invasive brain stimulation, and the selection between them should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s needs, anatomical considerations, and treatment goals rather than solely on general efficacy rates. Our experienced specialists at Mindset TMS help each individual select the safest and most effective treatment.
Mindset TMS Offers Top-Quality TMS Procedures in Greeley, CO
At Mindset TMS in Greeley, our distinguished team of mental health professionals delivers comprehensive TMS therapy. We combine cutting-edge technology with personalized treatment approaches supported by skilled nurse practitioners, certified TMS technicians, dedicated staff members, and a board-certified psychiatrist, Dr. Nicholle Peralta. Our comprehensive care model integrates innovative therapies with traditional psychiatric services, offering hope to individuals struggling with depression, anxiety, and OCD. With a mission focused on transforming mental health care, Mindset TMS provides a welcoming environment where patients can access advanced treatment options and expert guidance on their journey to recovery.





The staff is so friendly. Dr. Peralta really listens to me and how I am progressing with the treatment and is excellent at explaining the process and answering my questions.
Amazing office, great setting easy location and the Dr was amazing asked great questions and came up with a plan to make me feel better.
Dr. Peralta is very concerned and helpful, she listens and problem solves with you. She also explains TMS in an understandable, relatable manner which also put you at ease while reassuring you. The whole staff at Mind Set is very positive and supportive. I'm really happy I found Dr. Peralta and Mind Set, they have made a true difference in my life.
Dr. Peralta and her staff have continuously impressed me and my wife. We respect and appreciate everything that they do for us and they can definitely do the same for you as long as you follow their advice, help, and protocols.
Everything was conducted professionally. An explanation was given as to what and why everything was being done as it was happening so I felt very comfortable about what was going to happen.